fisetin
Zheng L.T., Ock J., Kwon B.M., Suk K. Suppressive ramifications of flavonoid fisetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation and neurotoxicity.
Syed D.N., Adhami V.M., Khan M.I., Mukhtar H. Inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling by the dietary flavonoid fisetin.
Lavasani M., Robinson A.R., Lu A., Song M., Feduska J.M., Ahani B. Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model.
- Kuntz S. Wenzel U. Daniel H. Comparative analysis of the effects of flavonoids on proliferation, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis in human cancer of the colon cell lines.
- The experience of caspase3/7 was assessed by luminescence intensity utilizing a multi scan plate reader .
- The chemical signals it gives off are pro-inflammatory cytokines, which become a source of low-level inflammation.
- Although considered of lesser significance, phenolic compounds also impart the color of plants.
Targeting amphiregulin derived from senescent stromal cells diminishes cancer resistance and averts programmed cell death 1 ligand (PD-L1)-mediated immunosuppression.
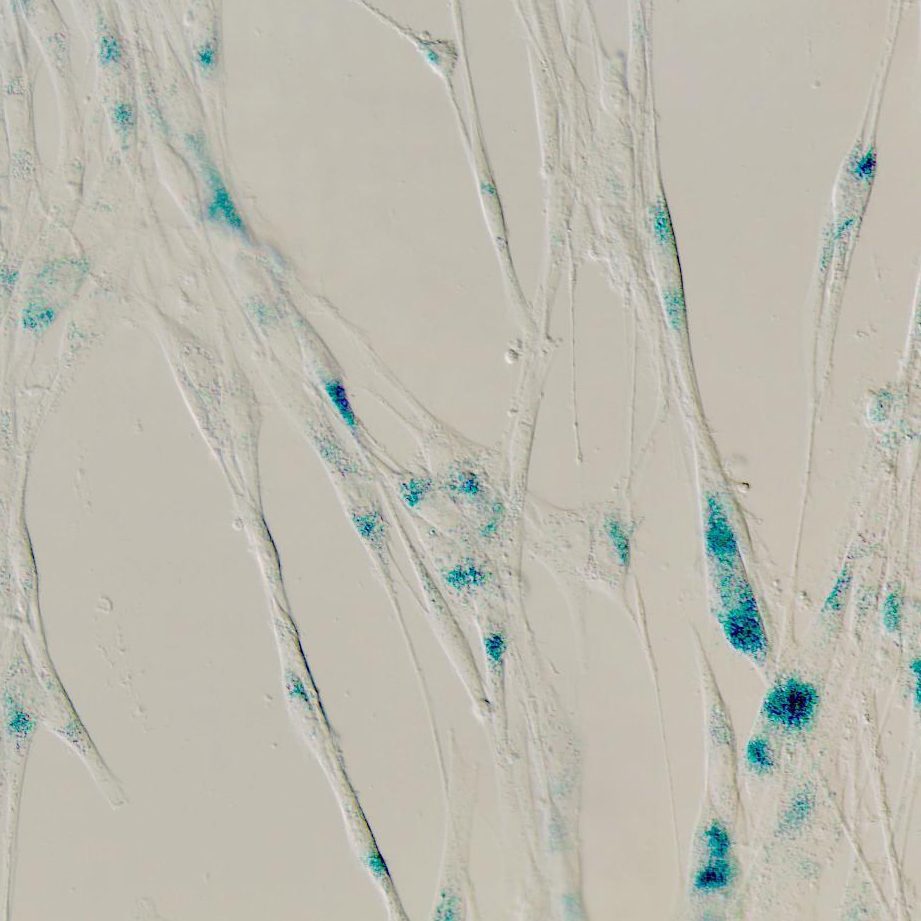
We next measured the capacity of GSE to differentially target senescent cells in a time course.
Upon treatment with GSE at a concentration of 3.75 μg ml−1, the viability of senescent cells did not significantly decrease until after 20 h.
The difference in viability between senescent cells and the control reached a maximum after 32 h, implying heterogeneity of intrinsic resistance to senolytics in senescent cell populations (Fig. 1d).
Therapeutic targeting of cellular senescence has a significant effect on disease pathogenesis.
It could be more effective at alleviating degenerative diseases and frailty progression than any available treatment options.
Polyphenolic flavonoids are protective against ageing-related degenerative diseases such as for example cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, with potential therapeutic applications.
How Come Cellular Senescence Important?
Urolithin B was shown to be the most efficient at inhibiting aromatase activity in a live cell assay.
Proliferation assays also determined that urolithin B significantly inhibited testosterone-induced breast cancer cell proliferation.
Chronic inflammation, however, which occurs with obesity or certain disease states, damages cellular components, and plays a part in ill health.
Quercetin exerts its inflammatory activity by inhibiting inflammatory enzymes, including cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase, as well as by decreasing prostaglandins and leukotrienes — well-known inflammatory mediators.
So as to understand the physiological mechanism underlying this aftereffect of fisetin, we asked whether fisetin could affect long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices from rat brains.
LTP can be an in vitro assay that’s considered to be an excellent model of how memory is formed at the cellular level .
Furthermore, age-related changes in cognitive function have already been proven to correlate with impaired induction and maintenance of LTP .
- On the other hand, the inhibition afforded by flavanones, such as for example hesperetin, had not been accompanied with the forming of cysteinyl-hesperetin adducts, indicating that it can be inhibited via direct interaction with tyrosinase .
- In addition, it helps cells get rid of their toxic debris by consuming them.
- These findings suggest fisetin could be a highly effective weapon in the fight against aging.
- Maher P. Salgado KF. Zivin JA. Lapchak PA. A novel approach to screening for new neuroprotective compounds for the treating stroke.
The naturally occurring phenolic acids are found free or conjugated, where in fact the most common conjugation is to a carbohydrate.
Align your wellbeing hacks together with your genes for optimal wellbeing & cognitive function.
Strawberries are by far the best food source of fisetin, followed by apples and persimmons.
Take into account that research on fisetin’s effects continues to be in the preliminary stages.
Source Data Extended Data Fig 2
Cotreatment with TRAIL and fisetin caused significant activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 and disruption of mitochondrial potential in these cells.
Fisetin increased the protein expression of the TRAIL receptor and decreased the activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB .
For example, the commonly consumed flavonol quercetin has been reported to inhibit neuroinflammation by attenuating nitric oxide production and iNOS gene expression in microglia and by preventing inflammatory cytokine production, thus preventing neuronal injury .
However, one of the major physiological metabolites of quercetin, quercetin-3′-sulfate, failed to demonstrate any anti-inflammatory action .
The radical scavenging and anti-oxidant capabilities of forty-one flavonoids were benchmarked against one another in DPPH and β-carotene/linoleic acid assays (BCLA—expressed as % antioxidant activity) .
The scaffold, 5d, Fig.3 was sufficient in itself to provide increased protection against oxidation in the β-carotene/linoleic acid assay.
Masking of the C3-OH in ring ‘C’ 6c, 6e–6f was in turn sufficient to ablate antioxidant activity.
As seen in the stilbenoids, the current presence of OH groups were required for radical scavenging.
Extensive structural modifications to the stilbenoid scaffold are permitted whilst still retaining as well as enhancing antioxidant activity, provided that the main element structural features required for activity are retained.
The shortening of telomeres plays a central role in the aging process .
Curcumin — the primary active compound in turmeric — has been proven to possess powerful cellular protective properties, which are related to its potent antioxidant effects.
Trending Topic:
 Market Research Facilities Near Me
Market Research Facilities Near Me  Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver
Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver  Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse
Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse  CNBC Pre Market Futures
CNBC Pre Market Futures  Best Gdp Episode
Best Gdp Episode  Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.
Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.  PlushCare: Virtual healthcare platform. Physical and mental health appointments are conducted over smartphone.
PlushCare: Virtual healthcare platform. Physical and mental health appointments are conducted over smartphone.  Mutual Funds With Low Initial Investment
Mutual Funds With Low Initial Investment  Jeff Gural Net Worth
Jeff Gural Net Worth  Robinhood Customer Service Number
Robinhood Customer Service Number