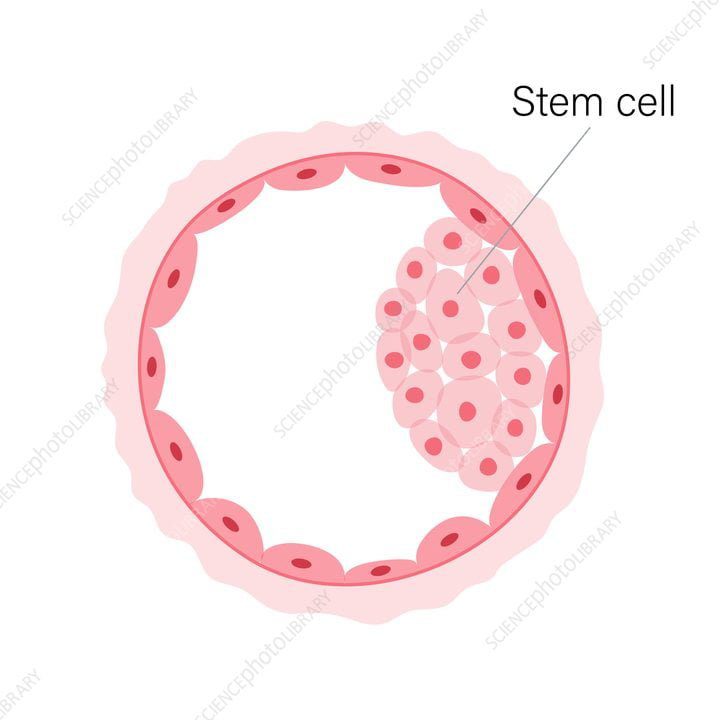
Organoids: Artificially-grown miniaturized versions of organs, allowing the micro-biology of diseases and treatments to be studied in laboratories.
The insert shows surface rendering of a dendritic spine structure on a GFP+ neuron with the pre-synaptic terminal labeled by SV2 staining in red.
Scale bars, 50 μm.
Shown in are sample recording traces of sEPSCs and pharmacological blockade by DNQX.
Identified sEPSC events are overlaid, and the common sEPSC trace is shown.
Also shown in is the summary of the percentage
- Beyond biochemical cues, stem cells also experience active and passive forces from their external microenvironment and convert these physical stimuli into biochemical responses18.
- Other researchers appeared to use organoids for cellular clusters that maintained the structural characteristics of the tissue of origin.
- At day 14, immunohistological analysis showed almost exclusive expression of forebrain-specific progenitor markers, including PAX6, OTX2, and FOXG1, with reduced expression of markers for other brain regions tested .
Using biochemical, cellular, and in vivo models we explore the cross talk between iron trafficking and RNA regulation mediated by poly C binding proteins and how these activities are modulated by disease.
We have several regions of research interest broadly in your community of immunomodulation using micro/nanoparticles and other carrier systems.
Accordingly, organoids generated from the patient with Alagille syndrome cannot differentiate toward the biliary fate, whereas in proliferate conditions, no differences were observed weighed against healthy controls (Andersson et al. 2018;Sachs et al. 2018).
Extracellular matrix 3D network of extracellular hydrated macromolecules, such as collagen and glycoproteins, present within all tissues and organs.
ECM provides essential physical scaffolding for cells, together with the biochemical and biomechanical support necessary for tissue morphogenesis, differentiation, and homeostasis.
- In addition, we try to know how transcriptional enhancers help orchestrate responses to external stimuli found in the tumor microenvironment.
- Once cells form an organoid, we’ve minimal input in cellular behaviour within the organoid.
- The roles of genetic versus physiological factors are examined.
The combination of organ-on-chips with gene editing and iPSC use for better control of genetic background is becoming an innovative, attractive alternative for the functional study of the cardiovascular system.
119 A good example was presented in a cystic fibrosis organoid model, where mutations in CFTR gene were repaired in intestinal stem cells by CRISPR/Cas9 system.
49 could actually recreate the increased ECM stiffness utilizing a photopolymerizable hydrogel while including the mechanical load similar to the stimulus that cardiac fibroblasts would experience under pro-fibrotic conditions.
The cyclic mechanical loading, together with the contact with a biochemical stimulus like transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) may also more closely mimic the fibrotic microenvironment of the heart.
There have also been non-microfluidic devices that make use of 3D cardiac tissue models to mimic hallmarks of cardiac fibrosis using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) along with fibroblasts.
Mastikhina et al.
Second, improving the controllability.
Beyond biochemical cues, stem cells also experience active and passive forces from their external microenvironment and convert these physical stimuli into biochemical responses18.
These physical cues arise from the matrix, external forces and/or cell–cell interactions.
Rather than relying on a natural or biologically derived ECM such as Matrigel with limited stiffness tunability, synthetic hydrogels or other ECM combinations can be leveraged
Trending Topic:
 Market Research Facilities Near Me
Market Research Facilities Near Me  Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver
Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver  Best Gdp Episode
Best Gdp Episode  Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse
Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse  Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.
Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.  CNBC Pre Market Futures
CNBC Pre Market Futures  Robinhood Customer Service Number
Robinhood Customer Service Number  90day Ticker
90day Ticker  pawfy
pawfy  Arvin Batra Accident
Arvin Batra Accident