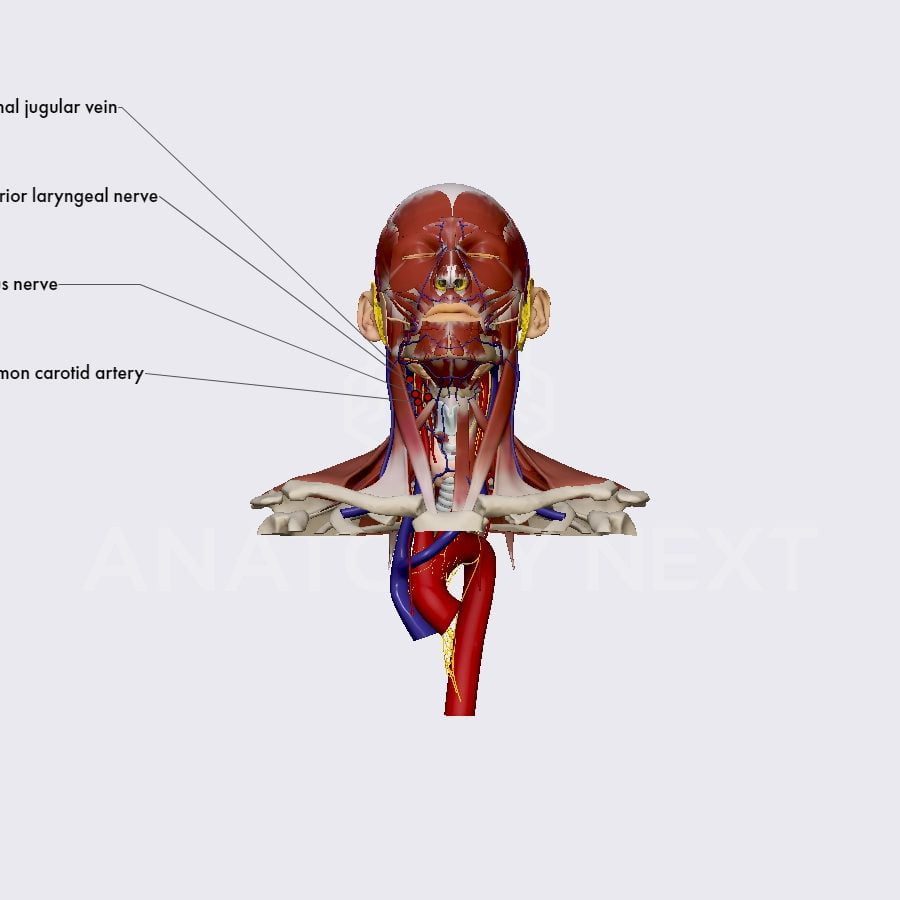
Vagus nerve stimulation: A medical treatment that involves the use of electrical stimulation to stimulate the vagus nerve, which is a major nerve in the body that is involved in many functions, including the cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Instead of a placebo/sham-arm, SoC was deemed the most likely control treatment that has been reflective of a real-world clinical scenario.
The open-label study design and short treatment duration may have contributed to a placebo effect in both treatment groups.
The 16.7 % response rate in the control group during the extension phase may partially reflect a placebo response to nVNS.
Through the vagus nerve, we respond to signals inside our environment in ways that calm, alarm, or dysregulate your body, and these states subsequently create emotional experience and play out in behavior.
Heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, all get into high gear, readying your body for movement.
The shifts in physiologic state in reaction to threat are kicked off by the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system.
Transcutaneous Cervical Vns
The vagus nerve is the main nerve of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Charles Conway, MD, a psychiatrist at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, told Verywell in an email what people are claiming online is in line with depression treatment.
He said nowadays there are five relatively large trials of vagus nerve stimulation that have all demonstrated a subset of patients with treatment-resistant depression respond to sustained vagus nerve stimulation.
Currently, aVNS has been explored in lots of of the diseases that VNS has been used to take care of.
- Stimulating the vagus nerve can influence the pain of migraine and arthritis, and subdue many resources of visceral pain.
- Transcutaneous stimulation can be achieved by attaching a vagal nerve stimulator to the ear to do something on the auricular branch of the vagus nerve.
- Low vagal tone is really a feature of inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, along with other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- This paper provides an overview of the neuroanatomy and neurochemistry relevant to the therapeutic uses of vagus nerve stimulation.
- a means of regulating the excitability of nerve cells.
Similarly, VNS can modulate the release of neurotransmitters and enhance neural plasticity.
For instance, VNS, through muscarinic receptors, influences cortical synchrony and excitability .
Additionally, repeatedly pairing VNS with a specific movement reorganizes the primary motor cortex and increases the cortical representation of this movement .
In 2010 2010, Hoeger et al. investigated the consequences of VNS on brain death-induced inflammation.
Specifically, the authors performed VNS on brain-dead kidney transplant donor rats and assessed its impact on graft outcome .
Anti‐inflammatory Properties Of The Vagus Nerve[edit
The principal outcome was the change in FuglMeyer Assessment Upper Extremity (FMAUE) score.
After 6 weeks, the mean FMAUE increased by 5.0 points (SD 4.4) in the VNS group and 2.4 points (3.8) in the control group.
After 3 months, a clinically meaningful response was observed in 47% of patients in the VNS group weighed against 24% of patients in the sham group.
Interestingly, the improvement with VNS was observed even in patients who experienced stroke many years prior (mean time since stroke was 3.1 years).
The concha is generally used because the ear target for aVNS; however, some claim that stimulation of the tragus could be more advantageous .
Stimulation of different regions of the ear can produce different effects which may impact a study’s results and reproducibility .
Additionally, multiple reflexes can be triggered during aVNS, specially the Arnold’s ear cough reflex, but additionally the ear-gag, ear-syncope, and ear-lacrimation reflexes .
A review encompassing 30 years of data suggests that VNS achieves optimal efficacy at six months of treatment with a 50–100% decrease in seizure frequency .
A large retrospective study using patient outcome registry data from over 4000 patients examined the consequences of VNS for the treatment of epilepsy based on patient age, epilepsy duration, and seizure type .
After a few months, a 46% decrease in seizure frequency was achieved with 44% of patients having at least a 50% reduction.
Patients less than 18 years old and those with a brief history of epilepsy of significantly less than 10 years achieved a more favorable response to VNS therapy weighed against older adults and those with an extended disease history.
Additionally, the largest benefit was achieved in people that have predominantly simple-partial seizures .
A multi-center randomized double-blind controlled acute treatment study comparing active and sham left cervical VNS in 235 patients with chronic TRD was subsequently conducted .
These patients had unipolar or bipolar disorder, and hadn’t responded to between two and six different antidepressant therapies.
Experimental And Clinical Application Of Invasive Llvns
Prolonged POCD occurs frequently after cardiac surgery, and the risk of POCD increases with age.
However, emerging evidences indicate that various inflammatory mediators get excited about the pathophysiology of POCD and inflammatory response might be a potential pathogenic factor.
Vagus nerve stimulation has been shown to decrease production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in both animal model and human.
In addition, CCK is essential for secretion of pancreatic fluid and producing gastric acid, contracting the gallbladder, decreasing gastric emptying, and facilitating digestion .
Saturated fat, long-chain essential fatty acids, proteins, and small peptides that derive from protein digestion stimulate the release of CCK from the tiny intestine .
There are various biologically active forms of CCK, classified in line with the number of proteins they contain, i.e., CCK-5, CCK-8, CCK-22, and CCK-33 .
In neurons, CCK-8 is always the predominating form, whereas the endocrine gut cells include a mixture of small and larger CCK peptides of which CCK-33 or CCK-22 often predominate .
In rats, both long- and short-chain fatty acids from food activate jejunal vagal afferent nerve fibers, but achieve this by distinct mechanisms .
Short-chain fatty acids, such as for example butyric acid have a direct impact on vagal afferent terminals while the long-chain essential fatty acids activate vagal afferents via a CCK-dependent mechanism.
The results measures included saliva spitted, Swallow Function Scoring System, Functional Oral Intake Scale, Clinical Assessment of Dysphagia with Wallenberg Syndrome, Yale Pharyngeal Residue Severity Rating Scale, and upper esophagus X-ray examination.
After tVNS, the individual was advanced to a full oral diet without head rotation or spitting.
Contents
Trending Topic:
 Market Research Facilities Near Me
Market Research Facilities Near Me  Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver
Cfd Flex Vs Cfd Solver  Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse
Tucker Carlson Gypsy Apocalypse  CNBC Pre Market Futures
CNBC Pre Market Futures  PlushCare: Virtual healthcare platform. Physical and mental health appointments are conducted over smartphone.
PlushCare: Virtual healthcare platform. Physical and mental health appointments are conducted over smartphone.  Best Gdp Episode
Best Gdp Episode  Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.
Stock market index: Tracker of change in the overall value of a stock market. They can be invested in via index funds.  Mutual Funds With Low Initial Investment
Mutual Funds With Low Initial Investment  Jeff Gural Net Worth
Jeff Gural Net Worth  Robinhood Customer Service Number
Robinhood Customer Service Number